Forensic Evaluation of Concrete
C3S Forensic Evaluation of Concrete Services
Forensic Evaluation of Concrete
Thanks to our expertise and experience we eliminate all guesswork in the event failure occurs. We use innovative techniques in forensic evaluation of concrete to accurately determine the cause of the problem. We deliver results based on investigation, testing and analysis. We compile and report all our findings in detailed and comprehensive manner.
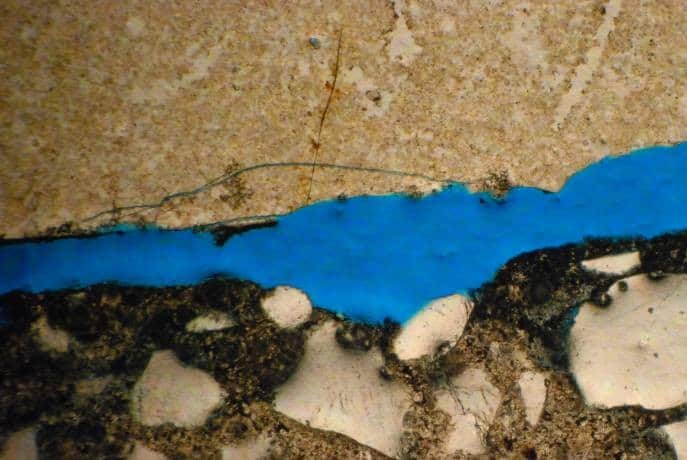
Petrographic Examination (ASTM C856)
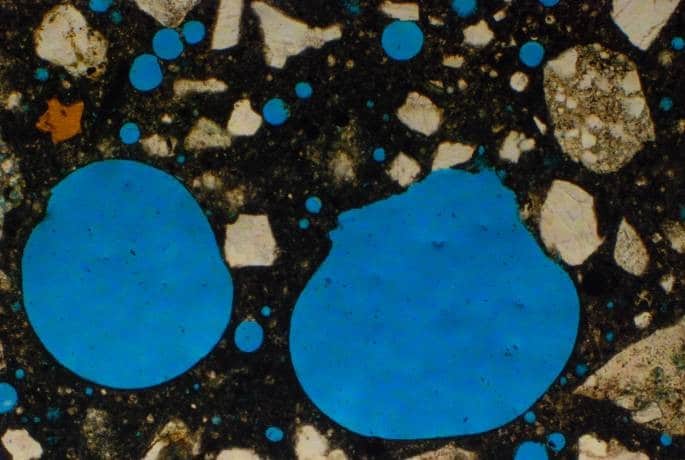
Petrographic examination is a critical part of a forensic evaluation of concrete. Petrographic analysis involves the optical examination of concrete specimen under low and high power magnification. Detailed instructions on conducting a petrographic examination of hardened concrete/mortar can be found in ASTM C856, “Standard Practice for Petrographic Examination of Hardened Concrete”.
Microscopic examination of concrete can identify deleterious or potentially deleterious components (e.g., strained quartz, sulfide minerals, etc.) within the aggregates; deleterious reactions within the paste (e.g., delayed ettringite formation) or between the aggregates and paste, such as alkali-silica reaction (ASR); and depth of paste carbonation relative to embedded steel reinforcement. Petrographic examination can also identify quality control issues associated with the mix (including unwashed aggregates, high water-cement ratio, and/or air content outside of specified or recommended limits) or improper finishing and/or consolidation of the concrete when it was placed.
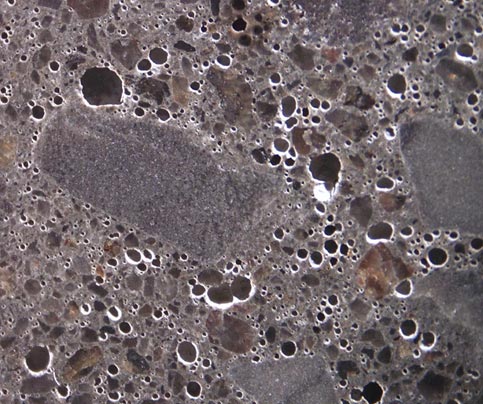
Hardened Air-Void Analysis (ASTM C457)
A robust air void system within hardened concrete will allow it to withstand freeze/thaw cycles and is therefore crucial for exterior concrete placed in severe climates. Conversely, hardened concrete without an appropriate air void system may ultimately crack or fail. The surface area, specific surface, spacing factor, frequency of air voids, total air content, and paste-air ratio of the concrete all play important roles in helping the concrete resist freeze/thaw damage.
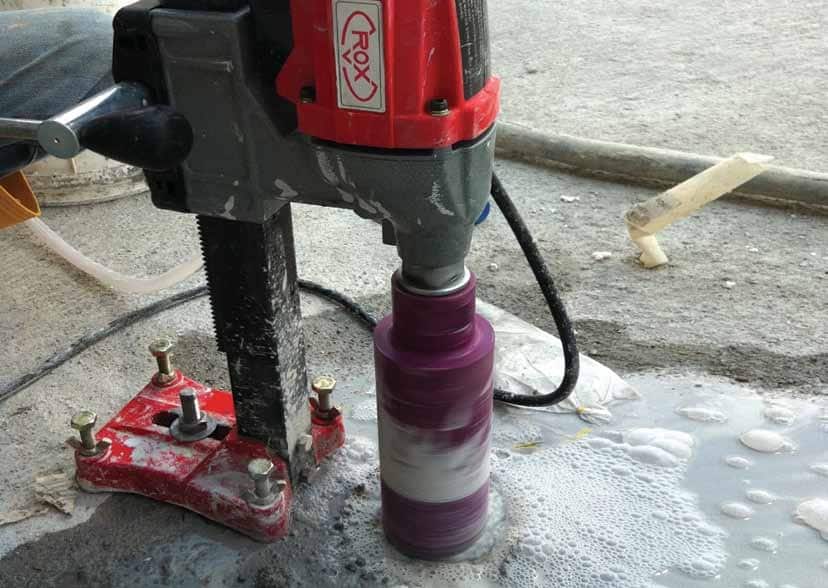
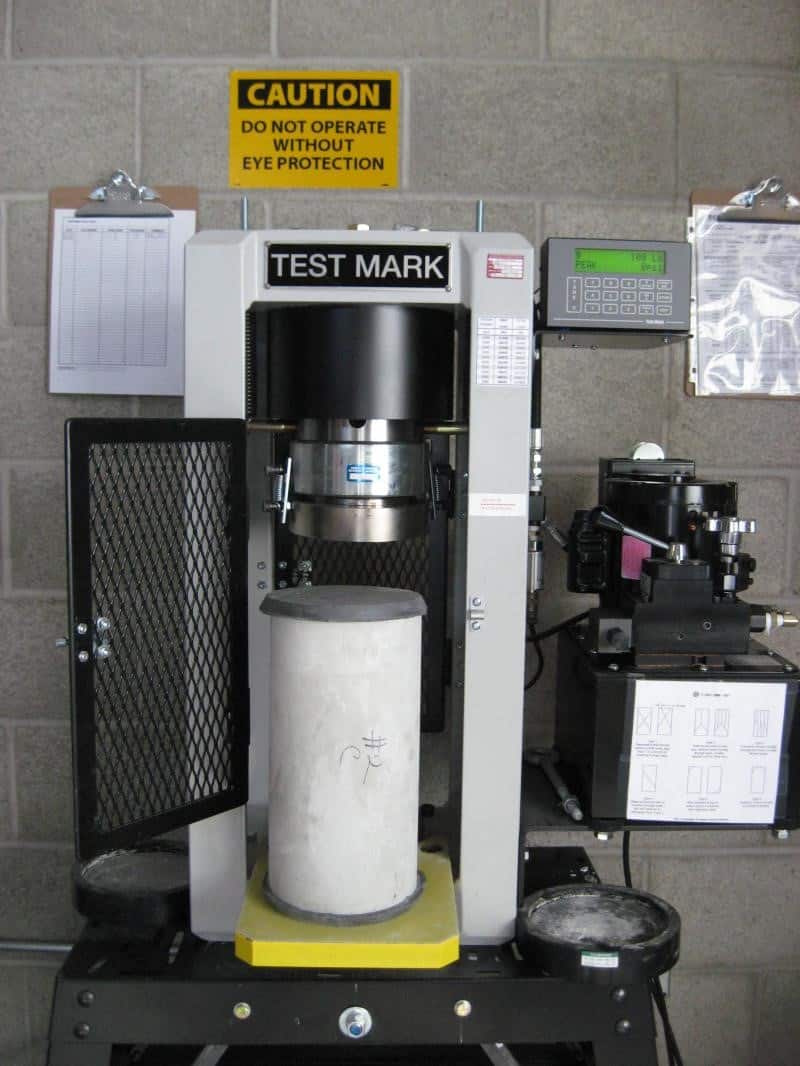
Compressive Strength (ASTM C39)
Determining compressive strength is important to forensic evaluation. C3S performs compressive strength tests utilizing the procedure set forth by ASTM C42 – Standard Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled Cores and Sawed Beams of Concrete. This test is performed to determine if the concrete meets the required compressive strength specified in the construction documents. Compressive strength is important to the forensic evaluation.
Water Soluble Chloride Content Test (ASTM C1218)
C3S performs this forensic evaluation of concrete test utilizing the procedure set forth by ASTM C 1152 – Test Method for Acid-Soluble Chloride in Mortar and Concrete.
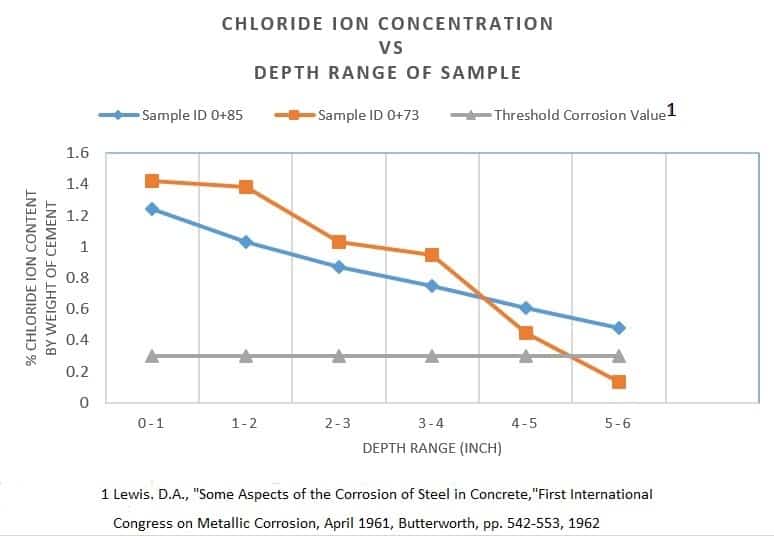
This test method determines the content of water-soluble chloride in new or existing cementitious mixtures. This test is used routinely in investigating potential for corrosion of embedded rebars in concrete structures. Especially in repair and rehabilitation of infrastructure where a portion of the structure is in sea/a body of water or pavements that have been subjected to salt application for ice removal.
This forensic evaluation of concrete method is often resorted to in assisting to determine the point within concrete where the critical chloride content to cause corrosion of rebar occur. Samples of concrete taken with a rotary impact drill at successive one-half inch depths are taken to the level of the rebar. The chloride content is separately determined for each depth and a graph developed to give the chloride ion profile in the structure.
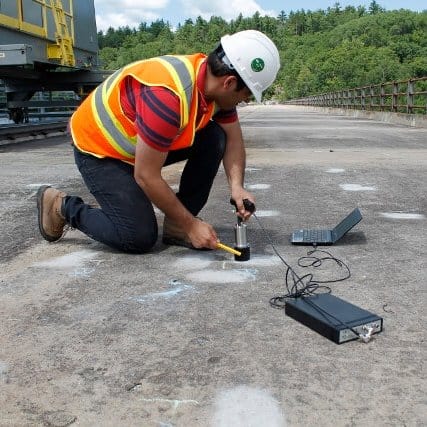
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) Scanning
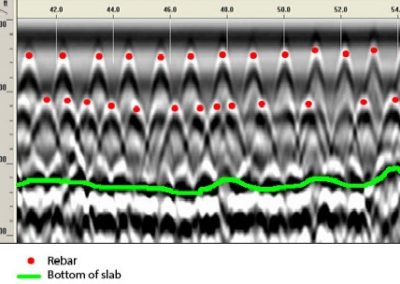
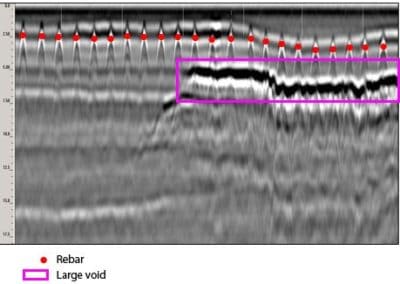
This forensic evaluation of concrete procedure utilizes a portable radar unit to determine the location and depth of steel reinforcement embedded in concrete, thickness of concrete members, presence of voids within or beneath a concrete slab, and assessment of the general uniformity of the concrete.
C3S provides ground penetrating radar scanning services which is a reliable, non-destructive means to locate targets within concrete structures prior to drilling, cutting or coring. By performing GPR on concrete, following can be assessed:
- Slab Thickness
- Concrete Cover and Rebar Location
- Voids – Location and Extents
- Pre Stressing Strands (PT Cables)
- Conduits
This is a standard ASTM test classified under ASTM D6432 – “Standard Guide for Using the Surface Ground Penetrating Radar Method for Subsurface Investigation” ( Section 1.1.2, point 11)
To complement our GPR service, we can also determine rebar size using the latest technology.
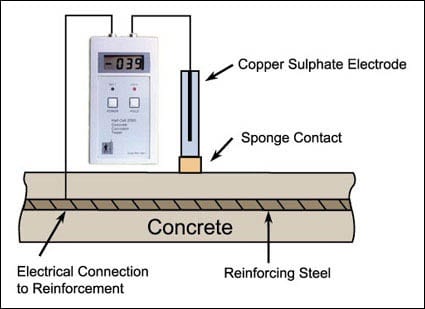
Half-Cell Potential Corrosion Testing (ASTM 876)
This forensic evaluation of concrete test method is used to determine the probability of active corrosion affecting the embedded steel reinforcement at the time of the test. Corrosion is an electro-chemical process that involves the movement of electrons. During the corrosion process, current flow (electron movement) produces a voltage potential around the corroding reinforcement. This voltage potential can be measured, and the probability of active corrosion can be evaluated. Areas with a high likelihood of corrosion can be identified by mapping out equipotential contour lines on the surface.
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) Testing
Another type of testing used in the forensic evaluation of concrete is Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) testing. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) testing is used to determine the integrity and quality of structural concrete or stone (up to 6 feet thick) by measuring the speed and attenuation of an ultrasonic wave passing through the element being tested. Areas with lower velocities typically have lower density and strength relative to high velocity areas. Data collected along multiple test paths can be used to create tomographic images of defects.
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Testing on concrete is a recognized non-destructive test to assess the homogeneity and integrity of concrete. With this ultrasonic test on concrete, the following can be assessed:
- Homogeneity or uniformity of concrete in structures, post construction to check for voids, honeycombs, cracks or other defects.
- Identify areas of low-quality concrete.
- Qualitative assessment of strength of concrete, its gradation in different locations of structural members and plotting the same.
- Any discontinuity in cross section like cracks, cover concrete delamination etc.
- Depth of surface cracks. We can define the size and shape of a defect by using multiple test paths.
This is a standard ASTM test classified under ASTM C 597 – “Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity through Concrete”
Sonic Pulse Velocity (SPV) testing is used at lower frequencies for distances greater than 6 feet, such as large columns, beams, and dams. We can test concrete, stone, or wood members up to 25 feet thick.

Condition Evaluation of Section of Bridge Deck
C3S performed UPV Testing for evaluation of a section of the 75’ long bridge deck that was suspected to have questionable quality due to an interruption during the concrete placement from an equipment failure.
The purpose of the forensic evaluation of concrete is to determine the variation in the quality of the concrete on the bridge for uniformity or the lack of it.

Study of Homogeneity of Concrete Columns at Industrial Plant in Freeport
The primary intent of the test is to determine the presence or absence of voids and or cavities in the hardened concrete columns by non-destructive testing using the Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity method.
Impact Echo Testing (ASTM C1383)
Another type of testing used in the forensic evaluation of concrete is Impact Echo Testing. Impact Echo Testing can be used to evaluate the depth of flaws (e.g., voids or delamination) in a concrete structure. It can also be used to determine the thickness of a concrete member, such as a slab or foundation wall. Impact echo testing can delineate areas of delamination and is applicable in many cases where only one side of the surface is accessible for testing.
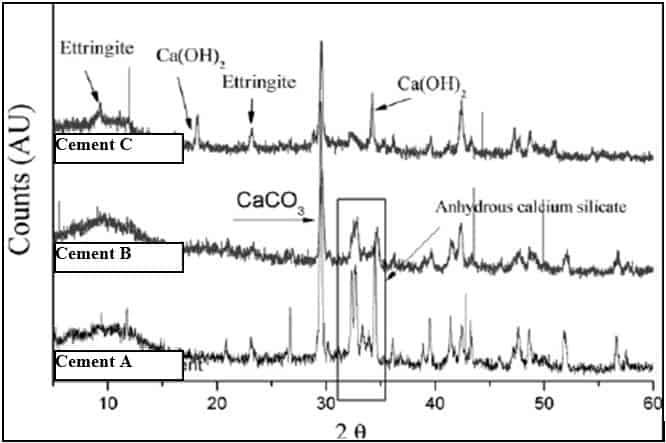
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
New to forensic evaluation of concrete, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis is a unique method in determination of crystalline materials such calcium hydroxide ettringite and others. XRD is primarily used for identifying crystalline material in investigative work in cement pastes and limestones in concrete. It is also widely used in several branches of sciences for similar applications.
A typical diffraction pattern for three types of hydrated cement paste give the results in the chart to the right:
C3S IS A GLOBAL LEADER IN CONCRETE EVALUATION
We provide quality services that our customers have come to expect.
Consulting Engineers
Concrete Experts
"C3S, Inc. is a concrete consulting firm dedicated to providing full scale services to civil, A/E firms, government entities, testing laboratories, property managers and owners, and other agencies dealing with projects related to concrete.
With its immense expertise, C3S. Inc. has been successfully serving clients in U.S and worldwide markets for over 30 years. "
CONTACT INFORMATION
C3S, Inc.
7100 Regency Square Blvd.
Suite 183
Houston, TX 77036
Office Hours
Mon-Fri: 8 AM - 5 PM
Sat-Sun: Closed