Aggregates
Aggregates
Aggregates
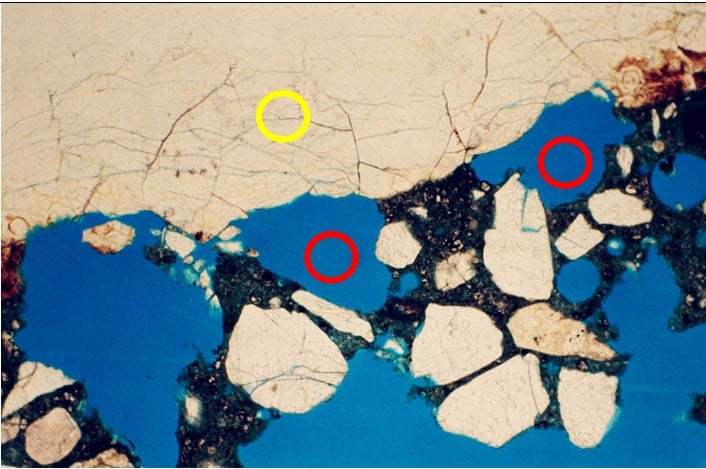
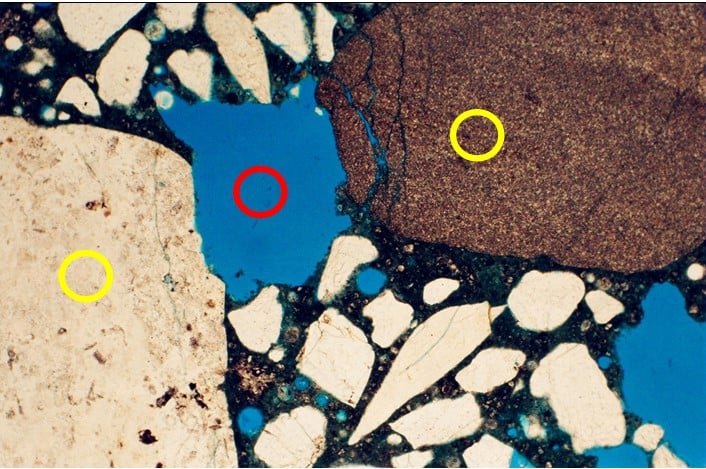
Aggregates – a rock – is used in many applications including, as filler for filling up voids during construction and in concrete. It is one of the most mined categories of minerals in the world. It is a crucial material for preparation of concrete. Types of rocks used for concrete include limestone, granite, gravel.
Concrete consists of about 60 to 75% of rocks hence a strong contributor to its properties. Physically, the rocks must be strong and durable. In the environment that the rocks reside in the hardened concrete it could be susceptible to chemical attack and thus must be tested to avert this situation. A chemical attack often result in crack formation and degradation of concrete.
Basic test for the physical is: i) The Los Angeles Abrasion test (ASTM C131) and ii) a test to determine chemically unstable minerals in the rock (ASTM C295)
The Los Angeles (L.A.) abrasion test Is a common test method used to indicate aggregate toughness and abrasion characteristics. Aggregate abrasion characteristics are important because the constituent aggregate on some projects i.e. pavements for highways and runways must resist crushing, degradation, and disintegration to retain a durable concrete.
Weathered rocks – rocks with inherent cracks in them – tend to chip off sections of the rock during mixing entrapping voids in the concrete to the detriment of the resulting concrete. Petrographic analysis is used effectively to identify the physical characteristics and furthermore, any potential deleterious minerals in the rock.
C3S IS A GLOBAL LEADER IN CONCRETE EVALUATION
We provide quality services that our customers have come to expect.
Consulting Engineers
Concrete Experts
"C3S, Inc. is a concrete consulting firm dedicated to providing full scale services to civil, A/E firms, government entities, testing laboratories, property managers and owners, and other agencies dealing with projects related to concrete.
With its immense expertise, C3S. Inc. has been successfully serving clients in U.S and worldwide markets for over 30 years. "
CONTACT INFORMATION
C3S, Inc.
7100 Regency Square Blvd.
Suite 183
Houston, TX 77036
Office Hours
Mon-Fri: 8 AM - 5 PM
Sat-Sun: Closed